The Real Reason You Bruise So Easily
Updated: Sep. 13, 2022
The occasional bruise is virtually inevitable, but those that show up with zero explanation can be alarming. Here's what may be causing them.
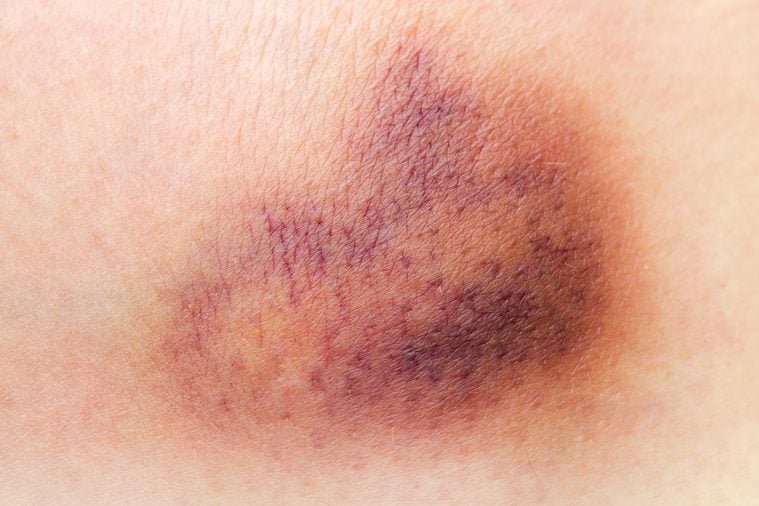
Everyone gets bruises. You can expect to see purple when you knock your leg into a table or jam your elbow into a wall, but if you have mysterious bruises appearing everywhere or lingering longer than a month, there could be a larger problem. According to the Mayo Clinic your genetics, medications, supplements and certain conditions can leave you more likely to bruise—but your love of the sun could also be to blame.
Get The Healthy @Reader’s Digest newsletter
The problem stems from a compromised part of your skin, which has three layers: the epidermis (the outer layer), dermis (the middle layer, which also contains spongy collagen), and hypodermis (the lowest layer). When you bump up against a hard object, you can burst tiny blood vessels called capillaries in your skin. They leak blood that gets trapped just below the skin’s epidermis, and the result is a colorful bruise.
The Doctor-Approved Way to Get Rid of Bruises ASAP
If your skin layers are strong enough, they can act as a barrier that protects those blood vessels and you’ll bruise less. However, the sun’s harmful UV rays can make you more susceptible to bruising. It breaks down your dermis’ cushy collagen, and without that padding, your capillaries are more vulnerable to impact.
Collagen also helps explain why women tend to bruise more easily than men—male skin has a thicker collagen layer. You can minimize bruising, notes the Cleveland Clinic; just make sure you meet your daily requirements for vitamins B12, C, K and folic acid. These nutrients help keep your capillaries strong and flexible.
Sunscreen is also key. It not only protects against sunburns, but it will also protect your collagen.
Here’s Exactly What to Look for in a Sunscreen
If you find that bruises continue to appear mysteriously, especially on your trunk or face, see your doctor: It could be a sign that your blood is missing key components that help it clot.
For more wellness updates, follow The Healthy on Facebook, Instagram, and Twitter. Keep reading:
















