
Right or wrong?
You know you should tilt your head back with a nosebleed and you should put ice on a burn. Or wait … should you? There are lots of medical practices we’ve heard through the years that we just follow, but many of them aren’t based in fact. Or for some of them, new research has changed what doctors believe. Take a look at these health practices—from how we give first aid to how we watch TV—and see which ones are right or wrong.

True or false: Not all heart attacks involve chest pain
TRUE: A study of more than 1.1 million heart attack patients published in the Journal of the American Medical Association found that 31 percent of men and 42 percent of women didn’t have any chest pain before being hospitalized. The American Heart Association recommends calling 911 for other symptoms, too, including shortness of breath, light-headedness, and pain in your arms, back, neck, jaw, or stomach. (Here are some more silent signs of a heart attack you might be ignoring.)

True or false: Being overweight shortens your life expectancy
TRUE: Researchers have long discussed the “obesity paradox,” because some research has suggested that overweight people have a lower risk of mortality over time compared to people who are underweight and those who are obese. However, a 2018 study published in the European Heart Journal looked at the body mass index (BMI) of more than 300,000 people. Researchers found that the risks of heart attacks, strokes, and high blood pressure increased as BMI increased. In an earlier study published in JAMA Cardiology, researchers found that overweight and obese people had a greater risk of cardiovascular disease and the obese people had a shorter lifespan than normal-weight and overweight adults.

True or false: You should put ice on a burn
FALSE: It’s important to immediately immerse a burn in cool (not cold) water or apply a cool, wet compress for about 10 minutes, suggests the American Academy of Dermatology. But don’t use ice, which can cause more skin damage. It can cause constriction of blood vessels, which makes the burn deeper. After cooling the burn area, wash with soap and water, apply petroleum jelly, and cover with a nonstick, sterile bandage.

True or false: Antiperspirants cause cancer
FALSE: Aluminum-based compounds in antiperspirants temporarily keep sweat from escaping by plugging up sweat ducts. Some research suggests that these compounds can be absorbed by the skin and have hormonal effects. However, a review published in Critical Reviews in Toxicology found no link between antiperspirants containing aluminum and an increased risk of breast cancer. (Find out some other things you think cause cancer, but actually don’t.)
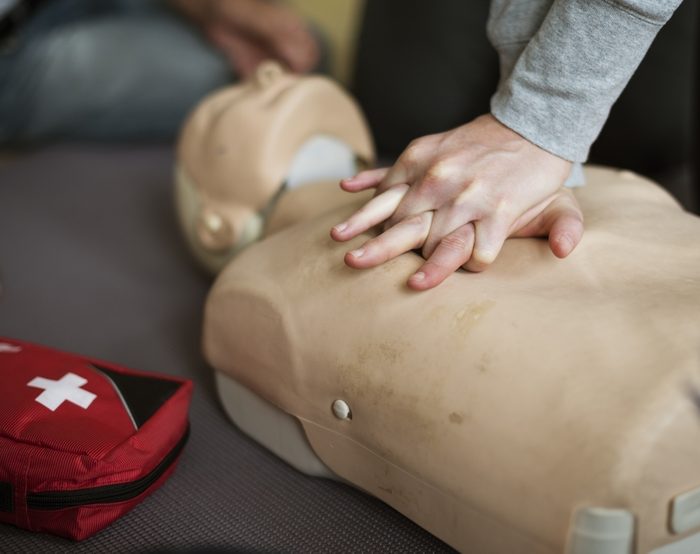
True or false: CPR doesn’t require mouth-to-mouth breathing
TRUE: A study of more than 27,000 people found that when bystanders gave CPR to people in cardiac arrest, survival rates were higher when they employed uninterrupted chest compressions rather than pausing for rescue breaths. “We have found that bystander-administered chest compression-only CPR, supported by telephone instruction, increases the proportion of people who survive to hospital discharge compared with conventional interrupted chest compression CPR plus rescue breathing,” the researchers wrote. (Here are 7 CPR steps everyone should know.)

True or false: Eating too much sugar will give you type 2 diabetes
FALSE: Sweet foods don’t directly lead to chronically high blood sugar. When you eat foods containing carbohydrates—including sugary foods—your body breaks them down into glucose, also called blood sugar. Your body makes the hormone insulin to keep glucose in check. Type 2 diabetes is caused by issues with insulin regulation, not with eating too much sugar. However, too many sweet foods can contribute to obesity, which is a risk factor for type 2 diabetes, so keeping a well-balanced diet and limiting treats is still the right idea.
Eating high-glycemic foods (particularly fructose) contributes to liver and hormone dysregulation which over time can lead to diabetes. Of course, it depends on the total diet and it is impossible to say that one food or micronutrient is responsible.
(Read more about how sugar can play a role in type 2 diabetes.)

True or false: You should keep someone with a concussion awake
FALSE: People have often believed that if someone has a concussion, you can’t let them fall asleep—or at least you have to wake them up every few hours to make sure they’re OK. The fear is that they could slip into a coma or lose consciousness. But now doctors advise that if the injured person is awake and able to hold a conversation, then it’s good to let them get rest, according to the University of Arkansas Medical School. The exception is children. Doctors advise you wake them up at least twice during the night to make sure they can be roused and that they have no other symptoms, like dilated pupils or trouble walking. (Here are 7 concussion symptoms you should never ignore.)
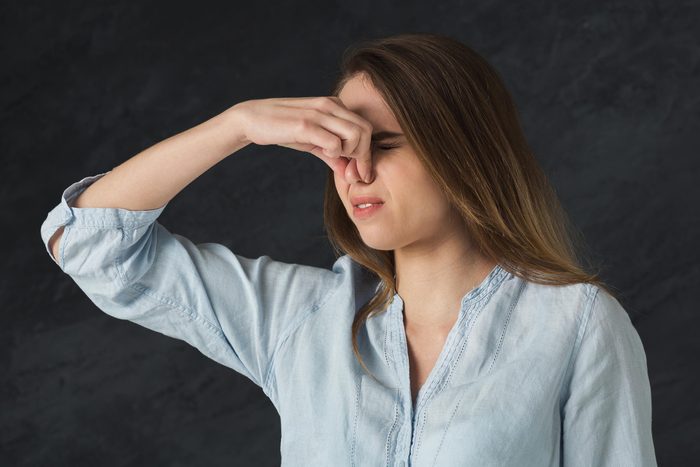

True or false: Tilt your head back if you have a nosebleed
FALSE: Tilting your head back might make you swallow blood, which could irritate your stomach, says the American Academy of Family Physicians. Instead, tip your head slightly forward. Use your thumb and index finger to firmly pinch the soft part of your nose shut. The soft part is between the tip of your nose and the hard, bony part that forms the bridge of your nose. Pinch for a full 10 minutes. If it’s still bleeding after 10 minutes, pinch it for 10 more. Once it stops, don’t bend over or blow your nose. See your doctor if it doesn’t stop after 20 minutes.
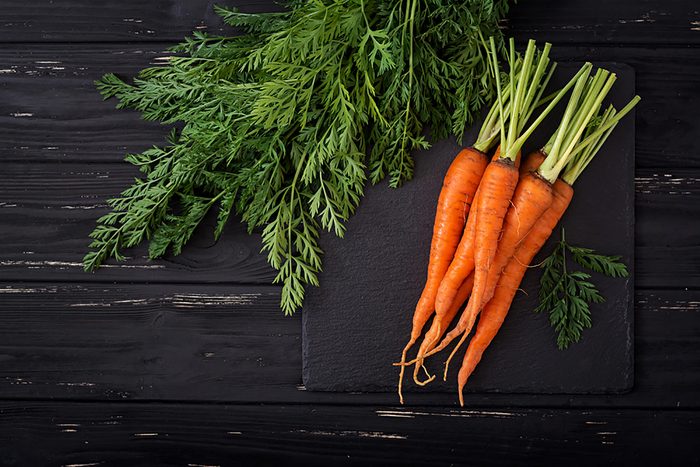

True or false: Carrots are good for your eyes
TRUE: Carrots won’t improve your vision, but they are rich in nutrients that have benefits for overall eye health. Carrots are a rich source of beta-carotene, a naturally occurring pigment that gives them their orange color. Beta-carotene is converted by your body into vitamin A, which is important for good vision. For eye health, eat foods high in vitamin A, including leafy greens such as kale and spinach.
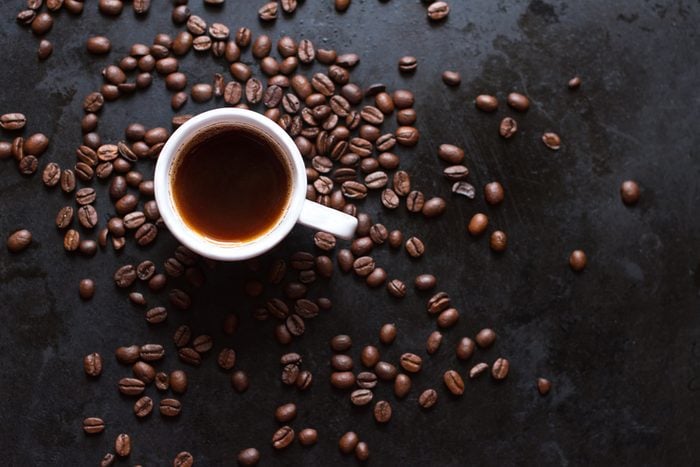

True or false: Coffee will dehydrate you
FALSE: The idea that caffeine is a diuretic that leaves your body short of fluids doesn’t hold water. In fact, studies show that coffee and tea drinkers are no less hydrated than people who drink water. A cup of coffee counts as part of your fluid intake and can actually help you hydrate. (Here are 8 more myths (and the truth) about how coffee affects your health.)
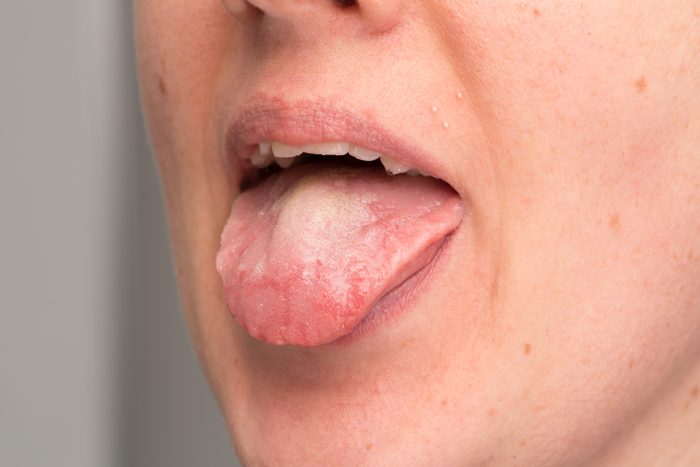
True or false: A person having a seizure can swallow their tongue
FALSE: A person having a seizure cannot swallow their tongue, says the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). If you put something in someone’s mouth like a spoon, it could injure their teeth or jaw. Instead, turn the person gently on their side to help them breathe, clear the area around them, and cushion their head with something soft like a folded jacket. This will also help keep them from biting their tongue which is common. (Know these unexpected things that can trigger a seizure.)
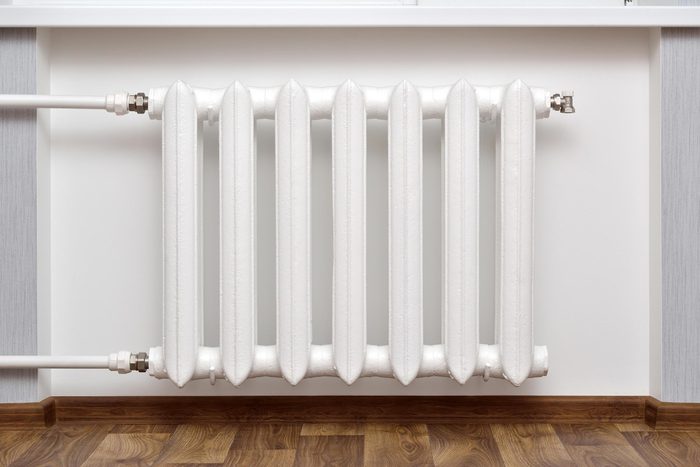

True or false: Frostbitten skin shouldn’t be warmed up by a heater
TRUE: Frostbite numbs the skin. It could burn without you realizing it if you use dry heat from a heating pad, fire, blow dryer, or radiator to warm the area. Instead, the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons suggests removing any restrictive clothing, then immersing the area in warm water. Be aware that the area may be very painful and it may swell and change color. Cover blisters loosely with a clean cloth and get emergency help. (Learn 7 frostbite symptoms you should never ignore.)

True or false: Stress is the main cause of ulcers
FALSE: The main causes of stomach ulcers are overuse of NSAID painkillers (such as aspirin and ibuprofen), infection from the bacteria H. pylori, and smoking. For years, people believed stress played a role, but then research findings suggested that it wasn’t a direct cause. A study in BMC Gastroenterology Stress finds that people who feel they are under high stress have more than double the risk of having a peptic ulcer than those who feel low stress. (Check out these surprising ways stress is good for your body.)

True or false: You should return to working out after a heart attack
TRUE: “Too often, heart patients use their condition as an excuse to cut back on physical activity when they should be doing the opposite,” says Salim Virani, MD, chair of the American College of Cardiology’s Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease Council. Trying to get 20 to 30 minutes of exercise most days can help strengthen your heart. Talk to your doctor about creating a safe routine. (Here are 15 easy ways you can walk more steps each day.)

True or false: Eggs are bad for your heart
FALSE: The old thinking was that cholesterol in food would raise blood cholesterol levels and, in turn, increase the risk of heart disease. A study of more than 400,000 adults in China published in the journal Heart found that eating an egg a day was associated with a lower risk of cardiovascular death compared to those who never ate them. Although this research exists, the answer isn’t 100 percent clear-cut. (And it doesn’t mean you should overdo it on the eggs.) Here’s more information on whether eggs are good for you. (Plus, want to add more eggs to your diet? Here are 54 delicious ways to eat eggs.)

True or false: Reading in dim light will harm your eyes
FALSE: It might tire your eyes out more quickly, but there’s no evidence that dim light will do any lasting damage, says Harvard Health. When reading, position light so that it shines directly on the page rather than from over your shoulder to reduce glare. (Learn these 11 signs your eyes could be in danger.)

True or false: Cracking your knuckles will give you arthritis
FALSE: Recent studies haven’t found a link between cracked joints and arthritis. The popping sound you hear is actually bubbles bursting in the synovial fluid that helps lubricate joints. But there’s still a chance this hobby isn’t harmless. Chronically cracking your knuckles may lead to a decrease in grip strength and there have been at least two published case reports of people injuring themselves while knuckle cracking. (Here are 10 surprising conditions your hands might predict.)

True or false: You don’t need eight glasses of water every day
TRUE: There’s no scientific evidence that eight is the magic number. You might need more or less than that, depending on factors such as climate and body size and your activity level. According to the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine, an adequate daily fluid intake is about 11.5 cups (2.7 liters) for women or 15.5 cups (3.7 liters) for men. That includes fluids from water, other drinks, and food. About 20 percent of fluids usually come from food, while the majority comes from drinks. To make sure you are getting enough, drink water throughout the day, especially if you are feeling thirsty. (Here are 8 surprising reasons you might be thirsty.)

True or false: Sitting up straight can be bad for your back
TRUE: “Hunching can certainly be bad for your back. But the opposite is true, too,” says Neel Anand, MD, professor of orthopedic surgery and medical director of spine trauma surgery at Cedars-Sinai Spine Center in Los Angeles. “Sitting up straight for too long without a break can also cause strain.” When you’re sitting, keep your lower back supported and your legs uncrossed with your knees at a 90-degree angle, and get up to stretch every half hour or so. (Here are 7 ways you can improve posture.)

True or false: People with dark skin can’t get skin cancer
FALSE: Dark skin is less likely to burn, but it isn’t immune to harmful UV rays and the damage they cause. People of all skin types need to use sunscreen. A study by the CDC found that black people were least likely to get sunburned, while white people were most likely to burn. Although the risk for sunburn is lower for dark-skinned people, they can get skin cancer. It is often diagnosed at a later stage, according to findings in the Asian Pacific Journal of Cancer Prevention, meaning it can be much deadlier. (Here are more sunburn myths that are damaging your skin.)
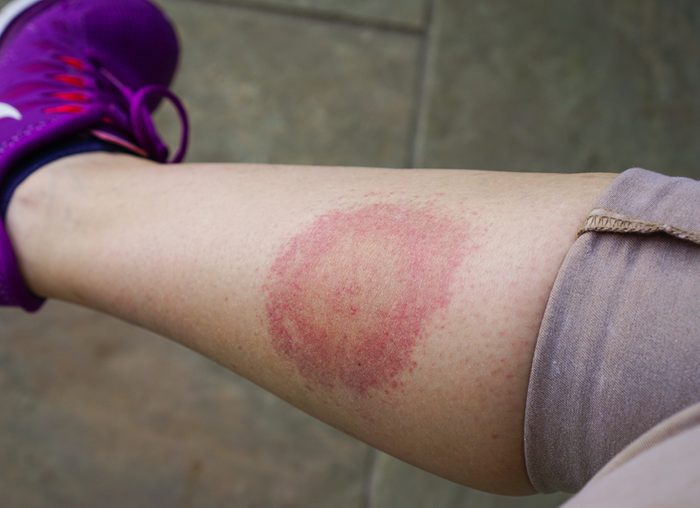
True or false: If you don’t have a bulls-eye rash, you don’t have Lyme disease
FALSE: About 20 to 30 percent of people with Lyme disease will never develop that classic rash, according to the CDC. Other symptoms to watch for include fever, chills, headache, achy muscles and joints, and swollen lymph nodes. (Check out these 18 silent signs you could have Lyme disease.)

True or false: You need less sleep as you get older
FALSE: Older adults often sleep less as a result of chronic conditions that are more common with age as well as the medications used to treat them. But that doesn’t mean they require less sleep. While sleep needs vary from person to person, the CDC recommends most adults get at least seven hours of sleep for optimal health.

True or false: Bar soap is covered in germs
FALSE: You might transfer germs to the soap while you scrub up, but they won’t last long enough to spread. An extensive study on the subject, published in 1965, found that bacteria on a bar of soap die within minutes and are not transmitted to the next person to use the soap. A follow-up study published in Epidemiology & Infection confirmed the original findings that bacteria from soap can’t be transmitted by washing hands. (Outside the bathroom, here are some of the germiest spots in your bedroom.)

True or false: Holding in a sneeze is unhealthy
TRUE: As your body gets ready to sneeze, pressure builds in your lungs. When your body tries to push the air out, it needs somewhere to go—and if you’re pinching your nose and mouth, it could be rerouted to the ears. Sneezing can propel air and droplets at as estimated speed of 100 miles per hour. When you hold a sneeze, pressure builds up. In one study published in Computers in Biology and Medicine, researchers found that holding in a sneeze can build up pressure as much as 24 times more than a normal sneeze. The journal BMJ Case Reports tells the story of a man who ruptured his throat when he held back a sneeze. (Check out these 13 weird things that make people sneeze.)

True or false: You can get the flu more than once a season
TRUE: Every year, there’s more than one flu strain circulating. Getting sick from (or being vaccinated against) one of them won’t protect you from the other strains. That’s why it’s important to take everyday preventive actions during flu season: getting a flu shot, covering your nose and mouth with a tissue while coughing or sneezing, washing your hands often with soap and water, and staying home if you feel sick. Not sure what you have? (Here’s the difference between the cold and the flu.)

True or false: Depression is incurable
FALSE: “Recovery from depression is not only possible; it’s actually likely when people receive the specific kind and amount of help that they need,” says Mark Henick, a mental health advocate and speaker. “When you combine medication with psychological therapy as well as social supports like housing, employment, and engagement, that’s the gold standard for recovery.” (Here are 10 foods that may help fight depression.)

True or false: You should rinse the toothpaste from your mouth after brushing
FALSE: When you rinse with nonfluoride mouthwash or water, you’re spitting out the fluoride that prevents tooth decay without giving it enough time to work. If you still feel like you need to rinse, studies suggest using a tiny bit of water to swish the toothpaste foam, then spitting it out. This will keep more fluoride on your teeth. Studies have found that keeping toothpaste remnants in your mouth can reduce tooth decay by up to 25 percent. (Watch out for these other little ways you’re brushing your teeth wrong, too.)

True or false: Sugar causes cancer
FALSE: It’s true sugar fuels all cells in the body—even cancer cells—but that doesn’t mean that eating less sugar will prevent or slow down cancer. Instead, the issue is eating too many calories from sugar, which can cause you to gain weight, according to MD Anderson Cancer Center. Being overweight is a risk factor for certain cancers and many diseases. Added sugars may contribute indirectly through hormone disruption and increased insulin.
Women should have no more than six teaspoons per day (100 calories), and men should have no more than nine teaspoons per day (150 calories), according to the American Heart Association. Most people have double that. (Here are some more cancer myths you need to stop believing.)

True or false: Running is bad for your knees
FALSE: You may think all that pounding takes a toll on your knees. But research published in Arthritis Care and Research found that recreational runners are not at increased risk of having symptoms of knee arthritis or other orthopedic problems. In fact, running may strengthen muscles that stabilize the knee, which may help prevent injuries and arthritis. (Here are 10 running mistakes you didn’t know you were making.)

True or false: Alcohol warms you up when it’s cold outside
FALSE: You might feel warmer and your face may start to flush as you sip that hot toddy, because alcohol causes your blood vessels to dilate, moving warm blood closer to the skin. But that’s just a feeling. In reality, blood supply is shifting throughout the body and you flush, causing your body to release more heat, according to a study in the journal Alcohol. Your liver releases heat as it metabolizes alcohol, which lowers your body temperature. Because you feel warm, you don’t shiver, so you don’t realize your temperature is going down. (Find out the safest amount of alcohol to drink.)
True or false: Women should be as worried about colorectal cancer as men are
TRUE: Colorectal cancer is the third most common type of cancer among men and women. Men do have a slightly higher risk overall: About one in 23 men will develop colorectal cancer, compared with one in 25 women, according to the American Cancer Society. (Learn 15 things cancer doctors do to avoid cancer.)

True or false: Sitting too close to the TV damages your eyes
FALSE: Sitting near your television set won’t hurt your eyes, but it may cause eyestrain, says the American Academy of Ophthalmology. Children are able to focus at close distances much more easily than adults which is why they often sit up close to the TV and it doesn’t hurt their eyes. Staring at anything for a long time can make your eyes feel tired, but it won’t do permanent damage. (Here are 6 ways you’re straining your eyes without realizing it.)

True or false: The flu shot might give you the flu
FALSE: Vaccines contain inactivated viruses, meaning the virus is no longer infectious. But to your immune system, it still looks like the flu virus in order to produce an immune response from your body, says the CDC. You might experience minor side effects after your shot, such as soreness or redness where you had the injection, or headache, fever, or muscle aches. The flu vaccine is the best way to avoid getting the flu, says the CDC. The agency recommends everyone over the age of 6 get the annual shot, unless they have an allergy to the vaccine. (Read on to learn 12 flu “myths” that are actually true.)
